Connecting to Oracle
Before starting
Before you begin, learn how to create a data source
Step 1: Create data sources
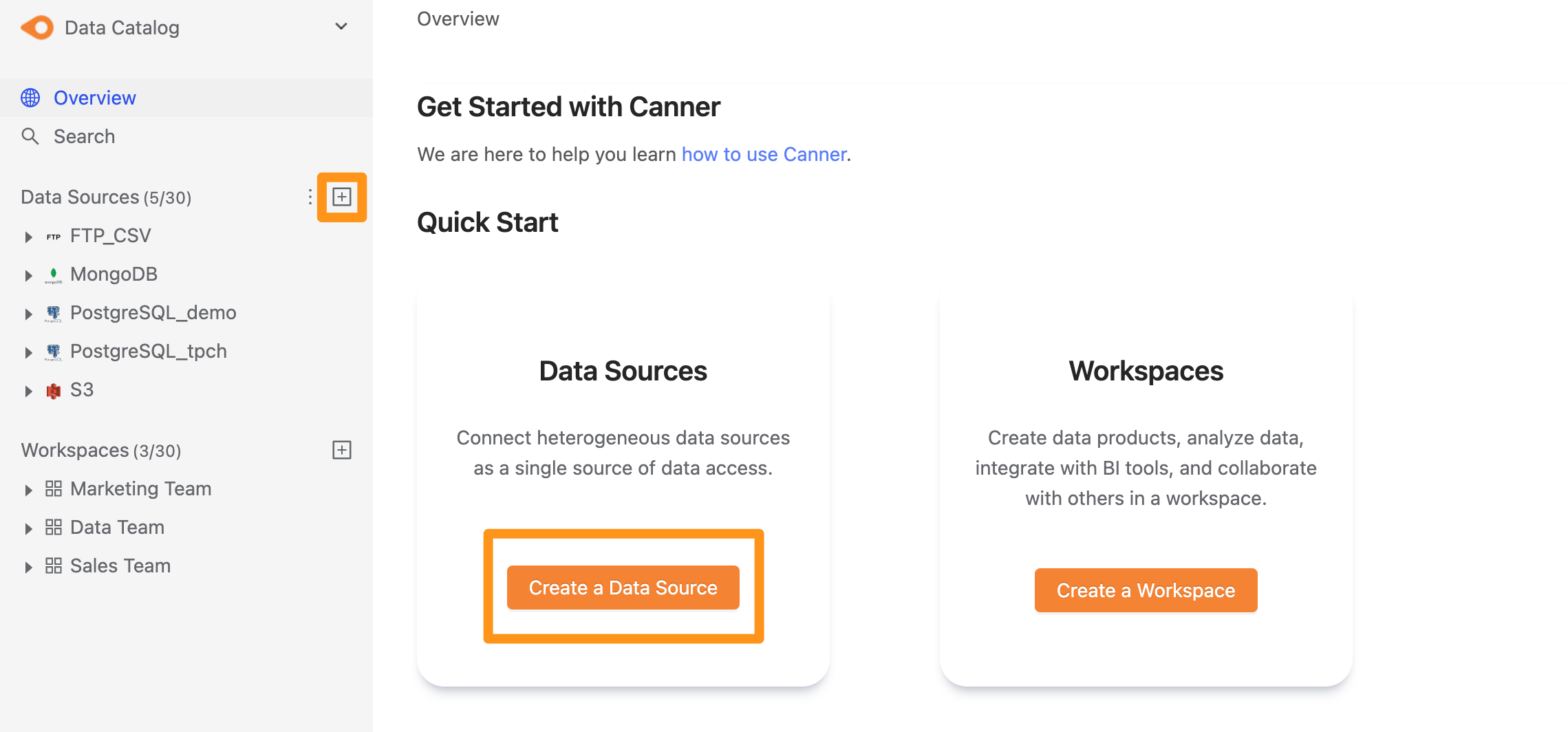
You can create a data source through the following two operations. The first is to click the "+" button on the sidebar Data Source or click the Create a Data Source button on the Overview page to create.
Step 2: Set connection information
In the pop-up form, fill in and set the connection information, and click Submit to send.
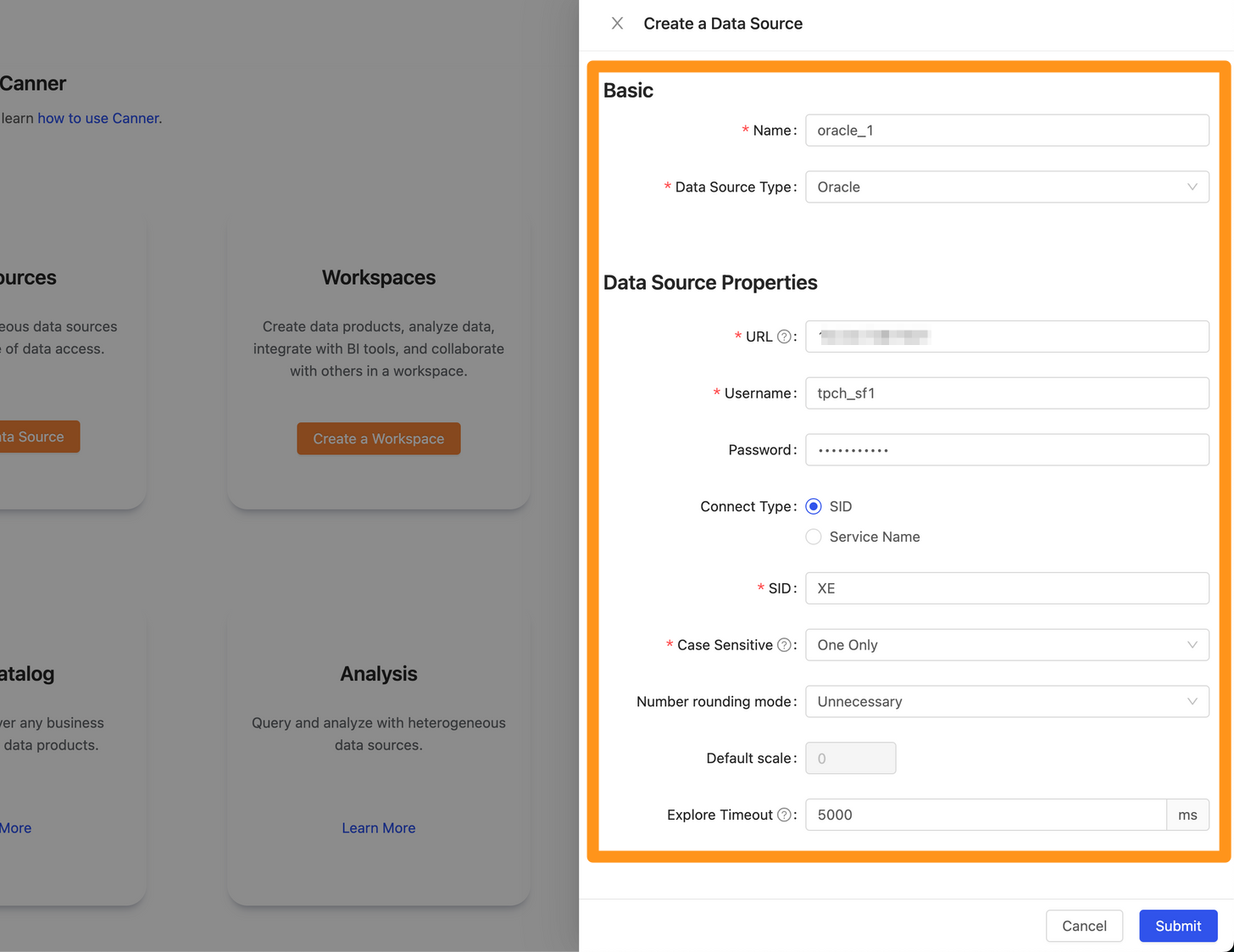
Name: database name, for display, can be modified laterData Source Type: database type, please selectOracleURL: Please fill in<hostname>:<port>format, for exampledatabase-1.cboscstksckj.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com:1521,10.207.64.3:1521Username: Username used for connectionPassword: Password used for connectionContent Type: use SID or SERVICE_NAME connectionSIDorService Name: According to the selectedContent Type, you can further inputSIDorService Name
Info
Table Pattern feature is only available after version 2.4.3
Table Pattern: Can use Java regular expression to filter the tables you want to connect. E.g.public.r.*for selecting all tables under thepublicschema whose names start with the letterr.Default ScaleandNumber Rounding Mode: If the Table contains floating point types, such asDouble,Float, and the data also has decimal point values, you need to set these two fieldsExplore Timeout: If the database contains a large number of Tables, it is recommended to increase this parameter so that the Explorer can wait for a longer time
Default Scale and Number Rounding ModeDefault Scale: How many digits to deal with the decimal pointNumber Rounding Mode: If it exceeds the number of digits specified byDefault Scale, how to deal with the excessUnnecessary: If the number of digits is exceeded, an error will be thrown directly to make the Query failUp: Round away from zeroDown: Round towards zero.Ceiling: Round towards positive infinity.Floor: Round towards negative infinity.Half Up: Round towards "nearest neighbor" unless both neighbors are equidistant, in which case round up.Half Down: Round towards "nearest neighbor" unless both neighbors are equidistant, in which case round down.Half Even: Round towards the "nearest neighbor" unless both neighbors are equidistant, in which case, round towards the even neighbor.
The following examples encounter different values. When Default Scale = 0, different Number Rounding Mode actually get the value
| Input Number | UP | DOWN | CEILING | FLOOR | HALF_UP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | throw ArithmeticException |
| 2.5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | throw ArithmeticException |
| 1.6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | throw ArithmeticException |
| 1.1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | throw ArithmeticException |
| 1.0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| -1.0 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 |
| -1.1 | -2 | -1 | -1 | -2 | -1 | -1 | -1 | throw ArithmeticException |
| -1.6 | -2 | -1 | -1 | -2 | -2 | -2 | -2 | throw ArithmeticException |
| -2.5 | -3 | -2 | -2 | -3 | -3 | -2 | -2 | throw ArithmeticException |
| -5.5 | -6 | -5 | -5 | -6 | -6 | -5 | -6 | throw ArithmeticException |
Step 3: Complete the build
After submitting, the Oracle data source will show up in the sidebar in a few moments, and you can click to enter the data source details page.